Comprehensive Guide to Breast Cancer Treatments
Explore a comprehensive guide to breast cancer treatments, including chemotherapy, radiation, and surgery—understand their roles, benefits, and what to expect.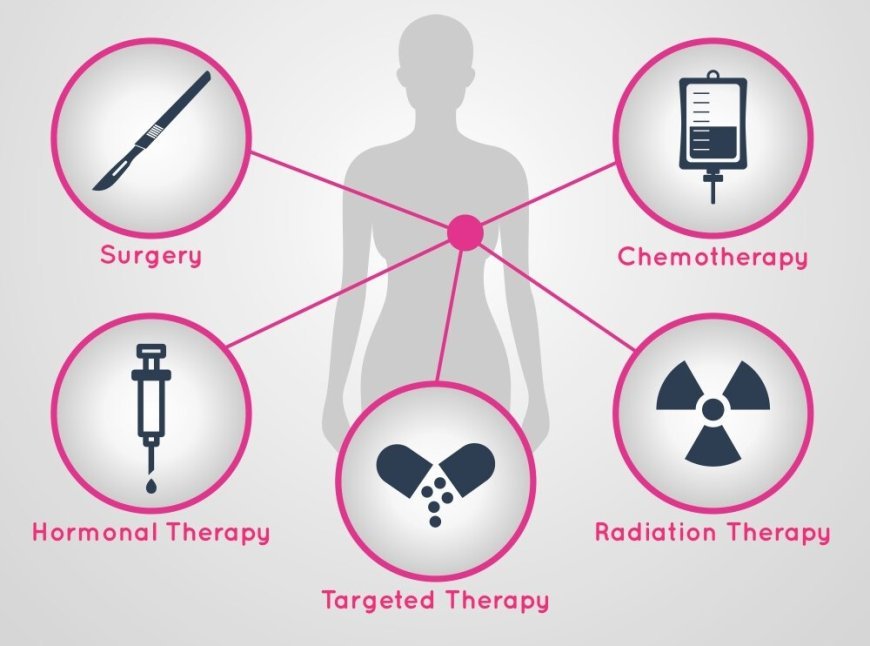
Being diagnosed with breast cancer can feel overwhelming. From the shock of the diagnosis to the flood of information about treatments, it’s easy to feel lost. One of the most important steps on the path to healing is understanding the available treatment options. Breast cancer is treated through various approaches, and the best plan often includes a combination of methods tailored to your specific case.
Three of the most common and effective treatments are chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and surgery. Each has its purpose, benefits, side effects, and role in a patient’s journey. This guide breaks down what each treatment involves, helping patients and families gain clarity and confidence in the decisions ahead.
Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer
Chemotherapy is often one of the first treatments people think of when they hear “cancer.” It involves using powerful drugs to kill rapidly dividing cancer cells. These drugs can be given orally or intravenously and are sometimes used before or after surgery or in combination with other therapies.
The purpose of chemotherapy varies depending on the stage and type of cancer. For early-stage breast cancer, it may shrink tumors before surgery. For later stages, it may be used to destroy cancer cells that have spread throughout the body. While it’s effective, chemotherapy can affect healthy cells too, leading to side effects.
• May be used before surgery (neoadjuvant) or after surgery (adjuvant)
• Targets fast-growing cancer cells throughout the body
• Common side effects include fatigue, nausea, hair loss, and lowered immunity
• Can reduce the risk of cancer recurrence
The effects and results vary by individual, but ongoing advances in chemo drugs have improved both outcomes and tolerability. It’s important to discuss options with your oncologist to understand the best approach based on your diagnosis.
Radiation Therapy for Breast Cancer
Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to destroy cancer cells left behind after surgery. It’s typically recommended after a lumpectomy and sometimes after a mastectomy, especially if the tumor was large or cancer was found in the lymph nodes.
Radiation is highly localized, meaning it focuses precisely on the breast area, minimizing damage to surrounding tissues. Treatments are generally quick and painless, often taking just minutes per session and spanning several weeks. The goal is to ensure that no microscopic cancer cells are left behind, reducing the risk of recurrence.
• Often used after lumpectomy or mastectomy
• Delivers high-energy rays to kill remaining cancer cells
• Usually given over several weeks
• Possible side effects include skin irritation, fatigue, and breast swelling
Patients undergoing radiation typically continue their normal routines. Side effects tend to be localized and resolve after treatment ends. Your radiation oncologist will guide the planning and process to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Surgical Options for Breast Cancer
Surgery remains a cornerstone of breast cancer treatment. The two main types are lumpectomy (breast-conserving surgery) and mastectomy (removal of the entire breast). Which procedure is right depends on the size and location of the tumor, patient preference, and whether the cancer has spread.
During surgery, lymph nodes may also be removed and tested to check if the cancer has spread. This step helps guide further treatment decisions. Breast reconstruction may be offered immediately or at a later time, depending on the type of surgery and the patient's wishes.
• Lumpectomy removes only the tumor and some surrounding tissue
• Mastectomy involves removal of one or both breasts
• Lymph node removal helps determine cancer’s spread
• Reconstruction options are available post-mastectomy
Surgery is often the first treatment step for many. It’s a critical part of physically removing cancer from the body and provides valuable information about how far the disease has progressed.
When Treatments Are Combined
Doctors often recommend a combination of treatments depending on the cancer’s stage, type, and individual health factors. For example, a patient might receive chemotherapy before surgery to shrink a tumor, followed by surgery and radiation to ensure all cancer is eradicated.
The combination of therapies works better in many cases than relying on a single treatment method. These multimodal plans are customized and adjusted based on patient response and side effects. Personalized care is the future of cancer treatment.
• Combining chemo, surgery, and radiation often improves outcomes
• Sequence depends on cancer stage and location
• Helps reduce recurrence risks and spread
• Tailored treatment plans offer more effective long-term solutions
It’s important for patients to ask questions and stay informed during each phase. Open communication with a cancer care team ensures you understand what each treatment means and how it supports your recovery.
Side Effects and Managing Them
Each breast cancer treatment comes with its set of side effects. While they vary by treatment type and individual, many are manageable with the right care. Understanding them helps patients prepare physically and emotionally.
Chemotherapy may cause fatigue, nausea, hair loss, and changes in appetite. Radiation can lead to skin irritation, breast pain, or fatigue. Surgery comes with pain, swelling, and limited movement temporarily. Thankfully, healthcare providers offer a variety of tools to ease these issues.
• Nutrition support and hydration help manage chemo effects
• Topical creams reduce radiation-related skin irritation
• Physical therapy improves movement after surgery
• Counseling and support groups help with emotional strain
Patients should report any side effects early. Modern medicine provides many options to lessen discomfort and maintain a high quality of life during treatment.
Targeted Therapy and Hormone Therapy
Besides the three main treatments, some patients benefit from targeted therapy or hormone therapy. These treatments attack specific types of cancer cells based on their unique markers. For example, HER2-positive breast cancer responds well to drugs that block HER2 receptors.
Hormone therapy is used when breast cancer cells grow in response to estrogen or progesterone. It can block the hormones or reduce their production in the body, helping to prevent recurrence. These treatments are often long-term and used alongside chemo or surgery.
• Targeted therapy attacks specific cancer cell receptors
• HER2-positive cancer responds well to HER2 blockers
• Hormone therapy prevents hormone-sensitive cancer growth
• Typically used in long-term treatment plans
Both therapies have significantly improved survival rates in breast cancer patients and offer alternatives to those who may not respond to conventional methods.
Understanding Recurrence and Monitoring
Even after successful treatment, breast cancer can return. That’s why follow-up care is essential. Recurrence may happen locally, regionally, or in distant parts of the body. Ongoing tests, imaging, and clinical exams help catch any changes early.
Doctors monitor hormone levels, tumor markers, and may order periodic mammograms or MRIs. Lifestyle changes, including nutrition and exercise, can also reduce recurrence risk. Patients are encouraged to stay proactive and attend regular checkups.
• Regular checkups and imaging help catch recurrence early
• Mammograms, MRIs, and blood tests are commonly used
• Lifestyle changes support long-term wellness
• Open communication with care team is vital
Recovery doesn’t end with treatment. Long-term health management is crucial in maintaining cancer-free living.
Emotional and Mental Health Support
Cancer is not just a physical disease—it affects mental and emotional well-being. Depression, anxiety, and fear of recurrence are common. Support from professionals, family, and survivor communities can make a profound difference.
Many hospitals offer counseling, therapy, and peer support groups. Activities like yoga, meditation, and art therapy also provide healthy outlets for emotional expression. Addressing mental health is just as important as physical recovery.
• Support groups offer connection and shared experience
• Therapy helps manage depression and anxiety
• Mindfulness and meditation improve emotional balance
• Family and friends provide essential encouragement
Seeking help is a sign of strength. Healing holistically ensures that survivors can move forward with confidence and peace.
Making Informed Decisions
Patients should always feel empowered in their treatment journey. Every individual’s cancer is unique, and no single path fits all. Asking questions, understanding each treatment, and weighing risks versus benefits are critical.
Doctors and specialists are there to guide but also to listen. Creating a personalized care plan that reflects your values, lifestyle, and preferences leads to better outcomes and a more positive experience overall.
• Ask detailed questions about each treatment option
• Seek second opinions if uncertain
• Understand risks, benefits, and recovery times
• Involve loved ones in decision-making if needed
Knowledge builds confidence. The more you know, the better equipped you are to face the journey ahead.
Conclusion
Navigating breast cancer treatment can be complex, but understanding the core options—chemotherapy, radiation, and surgery—helps patients take control of their care. These treatments, often used together, are powerful tools in fighting cancer and ensuring recovery. Supporting therapies, emotional care, and informed decisions round out a successful treatment plan. With the right information and support, patients can move forward with strength, hope, and clarity.
What's Your Reaction?